Welcome to day 9 of the 10 day Apex series. In the previous article we have seen Automating Actions in Salesforce using Apex Triggers. Now In this blog we will talk about Batch Apex and Scheduled Jobs.
As applications will start growing in complexity and we will require processing of large datasets or performing frequent tasks asynchronously becomes essential. Salesforce is providing developers with powerful asynchronous processing tools, such as Batch Apex for handling big data and Scheduled Jobs for recurring processes.
In this blog we will go through the fundamentals of Batch Apex that will illustrate how to write a Batch Apex class and scheduling Apex jobs using the Salesforce Scheduler.
What Is Asynchronous Apex in Salesforce?
Asynchronous Apex permits certain required processes to run in the background, different from real time user interactions, it will help to improve application performance and avoid hitting governor limits. These processes include handling large volumes of records, performing difficult calculations and automating daily, weekly or monthly tasks without obstructing the user’s existing workflow.
When Should You Use Batch Apex?
Batch Apex will be used for processing large sets of records where the volume is higher than the limits that can be handled by standard synchronous operations. Below are few scenarios:
- Data Cleaning or Transformation: Managing or updating millions of records that need updates.
- Difficult Calculations: Executing regular required calculations and aggregations that are resource intensive.
- Large Data Migrations: Migrating or archiving records that will not impact system performance.
- Integration and Data Processing: Synchronizing Salesforce data with external systems in batches so that process will work smoothly.
By processing records in smaller chunks by using batch, Batch Apex helps manage resource utilization and will stay within Salesforce governor limits.
Also Read
Don’t forget to checkout: Getting Started with Apex Triggers in Salesforce.
How to Write a Batch Apex Class in Salesforce
A Batch Apex class must implement the Database.Batchable<SObject> interface that will define three main methods: start, execute, and finish.
Batch Apex Method Breakdown: Start, Execute, Finish
- start Method:
The Start method is used to collect the records that need to be processed from the org. This will return either a QueryLocator (for SOQL queries) or an iterable set or collection of records. - execute Method:
The Execute method processes each batch of records. The required size of each batch can be defined when the batch is executed. - finish Method:
The Finish method will run after all the batches have been processed. It’s used for post-processing tasks, such as sending notifications, emails or logging summary information.
Example: A Simple Batch Apex Class
Below is an example that illustrates a Batch Apex class and will be useful to update a field on a collection of Account records:
public class UpdateAccountBatch implements Database.Batchable<SObject> {
// The start method returns a QueryLocator that retrieves Account records to be processed.
public Database.QueryLocator start(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
return Database.getQueryLocator(
[SELECT Id, Rating FROM Account WHERE Rating = 'Warm']
);
}
// The execute method processes each batch of Account records.
public void execute(Database.BatchableContext bc, List<Account> scope) {
for (Account acc : scope) {
// Update the status for each record in the current scope.
acc.Rating = 'Hot';
}
// Perform a DML update on the current batch.
update scope;
}
// The finish method can be used for post-processing once all batches are completed.
public void finish(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
// Optionally send a confirmation email or log the completion of the batch job.
System.debug('Batch processing is complete.');
}
}
Here’s an example of an Account before the job runs:
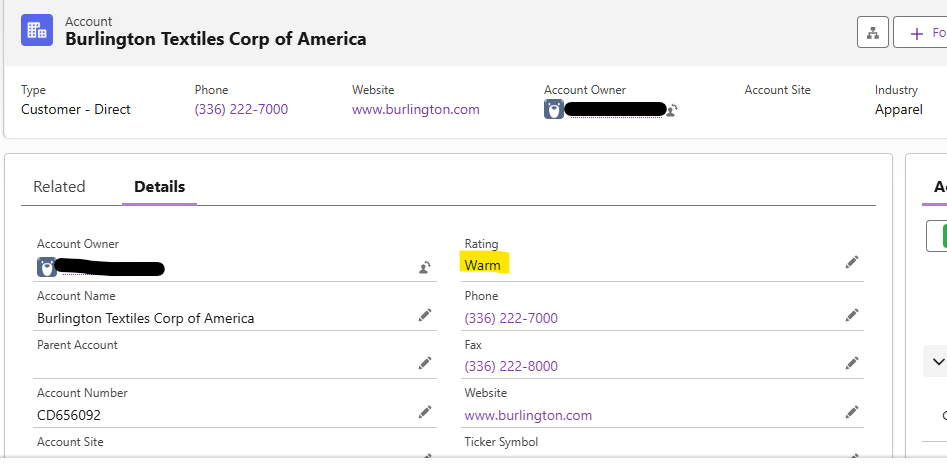
How to Execute a Batch Apex Job in Salesforce
A Batch Apex job will be executed by initializing the batch class and invoking the Database.executeBatch method. The second parameter defines the batch size for processing:
// Execute the batch with a batch size of 100 records per batch
Database.executeBatch(new UpdateAccountBatch(), 100);
With the help of the above simple example will demonstrate how a batch job retrieves Account records, processes them in small chunks like batches and updates the required field. It will provide a foundation for building more complex asynchronous processes.
Scheduling Apex Jobs Using Salesforce Scheduler
For regular or daily tasks, Salesforce provides the ability to schedule Apex jobs at specific times. The scheduling mechanism is useful when a process needs to run at a specific time or on a recurring basis, such as at required time data synchronization or routine maintenance processes.
The Schedulable Interface
To schedule an Apex class, the class must implement the Schedulable interface which requires a single method: execute. The execute method contains the logic that will run at the scheduled time.
Example: A Simple Scheduled Apex Class
Below is an example of a Scheduled Apex class that calls the Batch Apex class developed earlier:
public class ScheduledBatchJob implements Schedulable {
// The execute method schedules the batch job to run.
public void execute(SchedulableContext sc) {
// Instantiate the batch class and execute it with a specified batch size.
UpdateAccountBatch batchJob = new UpdateAccountBatch();
Database.executeBatch(batchJob, 100);
}
}
Scheduling the Job
Once we are implementing the Schedulable interface, we can schedule the job using the Salesforce user interface or using code. Scheduling using code is done by the System.schedule method this can be executed from anonymous window through developer console:
// Define a job name and a CRON expression for scheduling.
// In this example, the job runs daily at 2 AM.
String jobName = 'Daily Batch Job';
String cronExp = '0 0 2 * * ?';
// Schedule the job
System.schedule(jobName, cronExp, new ScheduledBatchJob());
Explanation of above CRON Expression:
- 0: Specifies the second at which the job will run.
- 0: Specifies the minute.
- 2: Specifies the hour in 24-hour format (2 AM).
- *: Every day of the month.
- *: Every month.
- ?: No specific value for day of the week.
The above CRON expression schedules the ScheduledBatchJob is planned daily at 2 AM. We may update the CRON expression as per the requirement.
Here’s an example of the Account after the job runs:
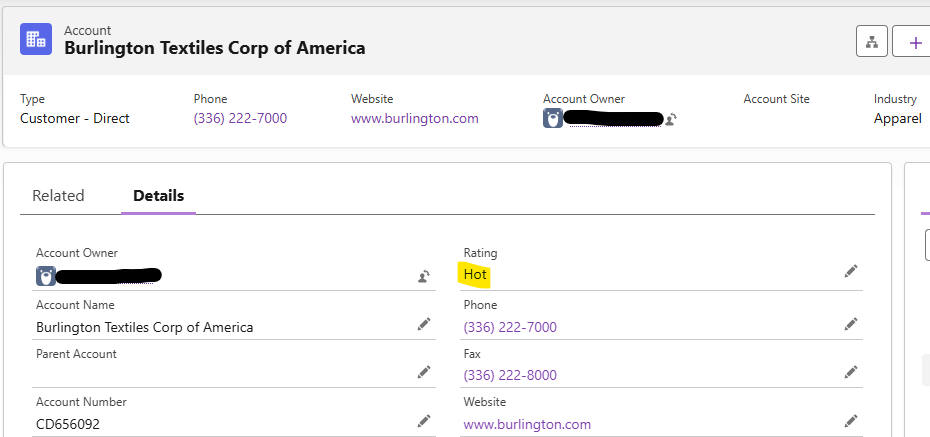
Best Practices for Batch Apex and Scheduled Jobs
To develop asynchronous processes using Batch Apex and Scheduled Apex, always follow below best practices if possible:
1. Bulkification
Execute batch jobs and scheduled processes to handle bulk data operations to keep inside of standard governor limits. Execute records in manageable batches and avoid performing DML operations or SOQL queries inside loops.
2. Error Handling:
Error handling within batch and scheduled processes. We can use try-catch blocks in the execute method to properly handle exceptions and log errors if any for investigation. We can use the finish method to trigger follow up actions (e.g., triggering an email alert if any issues).
3. Testing:
Write proper test classes for both Batch Apex and Scheduled Apex. We can use test methods to verify batch processing and job scheduling cases. Make sure that asynchronous processes complete successfully and handle tough or critical cases properly.
4. Resource Management:
Monitor the performance of asynchronous jobs. Utilize Salesforce tools like the Apex Jobs page to view job status and ensure that jobs run within acceptable time frames.
Conclusion
Advanced asynchronous processing by using Batch Apex and Scheduled Apex will be very useful for making scalable and well organized Salesforce applications. Batch Apex will handle large datasets by breaking records into smaller, manageable chunks.
While Scheduled Apex provides a mechanism to run repeated tasks automatically at specific times. By implementing these provided features and sticking to best practices such as bulkification, robust error handling and efficient resource management, we can build applications that perform critical data operations without interrupting user experiences or governor limits.
The examples provided in this blog provide a starting point for further complex learning. Developers can expand on these patterns to fit specific business requirements. Whether automating data updates or processing large batches of records for analytics and reporting at required time frames.
This is Day 9 of the Apex 10-Day Series: Advanced Apex: How to Use Batch Apex and Scheduled Jobs
On Day 10 we will discuss Apex Testing and Debugging. Stay Tuned, Happy coding















